Regional Game Industry Profile Berlin
According to the recent study “The German games industry 2019”, issued by the German Game Association in 2019, the city of Berlin, together with Hamburg, hosts the largest game industry in Germany in terms of the number of game studios and publishing companies, thus positioning Berlin in the mid-range of the BSR.
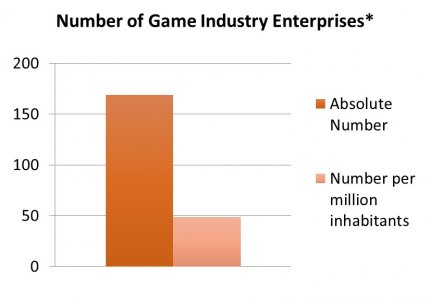
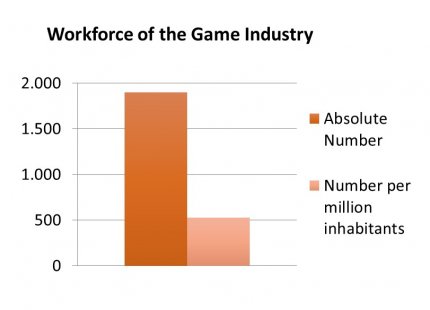
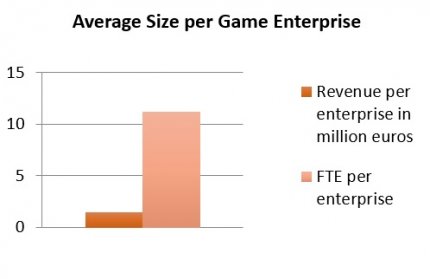
There are 175 enterprises (2017). With 1,900 people working in game development, Berlin has a 15% share of the industry in Germany. 72% of these are employees, of which roughly 1,300 people are full-time equivalents (FTE). This constitutes an average of 11 people per company. Taking a closer look at the size of the game enterprises, only four percent have more than 50 people working for them, indicating that small companies dominate Berlin’s game sector. The average revenue of the Berlin game developing companies is 1.85 m €, positioning Berlin in the mid-range of the BSR countries. However, the availability of game-specific incubation support in Berlin shows some room for improvement. The companies are as of today supported by three interest and lobby associations, five general technical incubators and a recent addition of a university incubator dedicated to games pre-seed and seed companies.
Source: Data from Game 2018, own chart.
*The year covered is 2017.
Source: Data from Hamburg Media School 2018, own chart
Source: Own calculation, own chart
| Interest/lobby associations | 3 |
| Incubators with full focus on games | 1 |
| Technical incubators that could in principle harbour game start-ups | 5 |
| Revenue | 255 m € |
Additonal information
Berlin is not only the capital of Germany, but also a federal state with its own government: the state of Berlin, which has a House of Representatives and the Senate. While the federal government has no ministry for culture, but only a state secretary in charge of coordinating common issues for German culture as a whole, each state has a minister or senator for cultural affairs.
Games are usually part of one or several clusters: media, ICT, creative industries, or digital businesses. Berlin has been named one of the most important hotspots for the game industry.
Based on several studies on the German game sector (published 2017 & published 2018) and on Berlin’s game industry (published 2018), Berlin has the highest number of game studios and publishers in Germany.
Berlin has about 118 developers and 57 publishers (however, companies that do both may have been counted twice, once for each role). Berlin is followed by Bavaria (including Munich) with 73 developers and 35 publishers.
However, studies show that Berlin is in particular a hotspot for young talents and indie studios. Still, there are a few larger companies: Yager, Wooga, GameDuell, King – and the new (third German) office of Ubisoft/Bluebyte.
In the last few years, Berlin has seen an increase in game companies opening subsidiary offices with a focus on publishing and marketing, such as Epic Games, Gamevil, Smilegate, Riot Games, Wargaming or Six Foot.
Berlin also offers more localisation services than any other German game hotspot region.
The comparative average revenue (in 2015) per game company also reflects the fact that the high number of game studios/publishers in Berlin includes a fair number of small companies: the average revenue is about 40% of what the average of the overall German revenue per company is. The figures are vague, as we do not have consistent figures for revenues and for the numbers of companies. But it is fair to say that the average revenue for Berlin is definitely much lower than the German average. In Berlin, a majority of small companies and start-ups have annual revenues below 1 m €, whereas the state of Hessen – with less than half of the number of companies but the highest revenue in Germany – has an average revenue per company of over 10 m €.
There were 1,900 people working for/with games studios and publishers, of which approx. 1,400 were employees, 92% of whom were working on a full-time basis.
Several large companies in Berlin employ one third of the people working in Berlin’s development/publishing segment: Wooga: 200 (2019), GameDuell: 150 (2019), Yager: 100 (2019).
The lack of headquarters of larger companies and anchor companies is indicative of the situation of Berlin’s game industry. Perhaps the strong presence of start-ups and small studios explains the stronger involvement of game developers in other digital content services (VR, AR, data analytics, social marketing etc.) than in other German cities. This also explains why only 77% of the game companies’ revenue is based on games sales. 23% are “other” types of revenue.
Most companies (90%) are independent, i.e. not part of a corporate group, and constitute the traditional civil-law entity. The favourite legal forms are “GmbH” (capital min. 25,000 €) and “UG” (minimum capital 1 €), the latter being close to the British format Ltd; it was not introduced until 2008.
Only 7% of the Berlin companies have headquarters or a parent company outside Germany. Not surprisingly, Berlin shows the lowest average company age at 4.2 years.
In support of a favourable economic climate, there are a lot of events, network activities and lobbyists in Berlin. Most notable is the organisation media.net berlinbrandenburg e.V. with its large and very active network, including the network games:net and their project BerlinBalticNordic.net.
The Senate Department for Economics, Energy and Public Enterprises is in charge of the public support of business and organises this support in clusters. Games are part of the ICT cluster with dedicated staff for this sector of the cluster. The Senate Chancellery is in charge of the media support, which includes the Games sector. Together they define the “political and support strategies for games”.
Berlin Partner for Business and Technology is a PPP with the state of Berlin and also has a person in charge of game businesses.
Berlin also hosts in a bi-annual rota the renowned German Computer Game Award and the annual Gamesweekberlin, the umbrella event for a whole range of successful formats such as Quo Vadis, A MAZE., Womenize or Media Award for Games.
______________________
Status: 2020
- game – Verband der deutschen Games-Branche e.V. (2019): The German games industry 2019
- game – Verband der deutschen Games-Branche e.V. (2019): 2018 A Guide to the German Games Industry
- Hamburg Media School Forschungs- und Kompetenzzentrum Audiovisuelle Produktion (2018): Die Computer- und Videospielindustrie in Berlin
- Hamburg Media School Forschungs- und Kompetenzzentrum Audiovisuelle Produktion (2017): Die Computer- und Videospielindustrie in Deutschland. Daten – Fakten – Analysen
- Gameswirtschaft (2016): Die 25 größten Spielehersteller in Deutschland
- Gameswirtschaft (2018): Deutschlands größte Spielehersteller 2018
- https://www.gamescapital.berlin/about/
- https://www.gamesmap.de/